If I get called a bot, I might start taking it as a compliment
Revolutionizing the gaming creation and experience with AI
Check out the evolution of gaming NPCs:
AI-driven games are going to be insane, but “bot” will continue to be an insult for a little longer.
Have you played Square Enix’s “The Portopia Serial Murder Case”? If you haven’t, don’t bother. It’s received dogshit reviews – even worse than Redfall (the 2023 benchmark for crappy games).
Let’s forgive Square Enix on this one though. They’ve released it alongside the statement that the game is an “educational demonstration of Natural Language Processing (NLP), an AI technology”. As Winston Churchill himself said, “success consists of going from failure to failure without loss of enthusiasm”.
So what does success in AI gaming actually look like? Let’s explore together how AI could revolutionize the game production industry. We’re going to get a bit technical, so strap in!
Regardless of the physical hardware that you use to play games (your phone, computer, or console), video games generally include three components: the Creator, the Game, and the Player.
Connecting these components are (1) the Production Process, and (2) Interaction.
1. Production Process
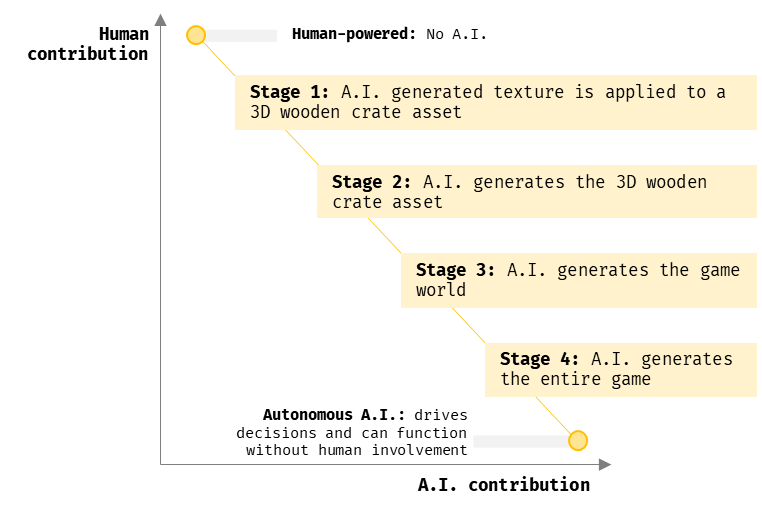
I’ve put together a table below that summarizes potential use cases for AI within each production stage:
Whilst the use cases of AI may currently be somewhat “simple” currently, increasing sophistication of AI models may result in cross-pollination of use cases, as illustrated below:
2. Interaction
The more exciting part for the average population (who sits on the “Player” side, rather than the “Creator” side), is how A.I. may change the way we interact with games.
Interaction is a result of physical input (e.g., player presses the spacebar on their keyboard) or physical output (e.g., on the player’s monitor, the player can see their character jump). Whilst having some form of physical hardware for input and output is unavoidable, the information and data that is (a) inputted, (b) processed, and then (c) outputted, could be significantly different when leveraging AI.
We’ve seen a key use case implemented in “The Portopia Serial Murder Case”:
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP involves enabling machines to understand human language. NLP includes the following subsets:
Natural Language Understanding (NLU), whereby a machine can analyze text or speech to determine the meaning of a sentence; and
Natural Language Generation (NLG), whereby a machine can generate a human language response.
Instead of a pre-scripted conversation, why don’t you ask the NPC a question?
Real-Time Feedback
AI provides the ability for games to provide real-time feedback, and this could go far beyond deciding the next chess move.
As we’ve seen in the production process, the ability to generate on-demand visuals, audio, text, and even game mechanics or storylines, could provide a new meaning to “open-world” games.

With this all in mind, my dreams of playing Sword Art Online may finally become a reality.